Recently, I've seen lot of videos surfacing online on social media sites likes YouTube Shorts and Instagram Reels, which have satisfying videos in background and an AI voice speaks to you with captions. Video tells you about some facts or some quick information about some country, movie etc.
The script is so simple and easy that you can generate it with ChatGPT or Gemini AI. Then you need to generate some AI voice (or you can you your voice too) and then get some satisfying videos from royalty free websites and Boom! You need to spend a little time editing and your video is ready.
While this might seem easy, how about if we automate the complete flow, wherein you just need to enter the title of the short you want to make, and the whole video will be generated within minutes!
Today, I've decided to make this tool using Python, as we can use MoviePy library to edit and render the multimedia content.
But before that, let's see the flowchart of how things will work.
- Enter the topic
- Generate script for the topic (using AI)
- Convert the script into Audio (Text to Speech)
- Add satisfying videos to background (same length as of generated audio clip)
- Add captions with smooth transitions to hook user attention
- Render the video and get MP4 output
Step 1: Topic
Step 2: Using Gemini API in Python
Step 3: Generating Audio
Step 4: Adding Videos
Step 5: Adding Captions
Step 6: Rendering
Final Code
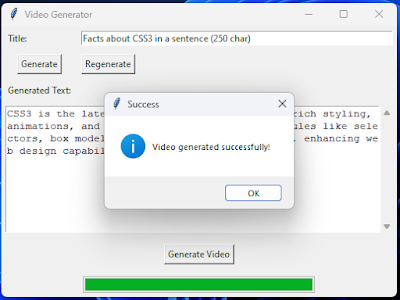
import tkinter as tk from tkinter import messagebox import tkinter as tk from tkinter import ttk, scrolledtext, filedialog, messagebox import requests import json import os os.environ['IMAGEMAGICK_BINARY'] = r"C:\Program Files\ImageMagick-7.1.1-Q16-HDRI\magick.exe" from PIL import Image import random import moviepy.editor as mp from moviepy.editor import * from moviepy.video.tools.subtitles import SubtitlesClip from pydub import AudioSegment import io # Import io for handling binary data from PIL import Image, ImageTk from google import genai import librosa import numpy as np import threading import queue class CaptionAdder: def add_captions_to_video(self, video_clip, text_prompt, audio_file, progress_queue=None): """Adds captions to the video clip, displaying 2 words at a time, synced with audio.""" try: # Load audio file using librosa y, sr = librosa.load(audio_file) audio_duration = librosa.get_duration(y=y, sr=sr) # Get accurate audio duration except Exception as e: print(f"Error loading audio or getting duration: {e}") audio_duration = video_clip.duration # Fallback to video duration words = text_prompt.split() num_words = len(words) # Calculate duration per word if num_words > 0 and audio_duration > 0: word_duration = audio_duration / num_words # Duration per word else: word_duration = 1.0 # Default duration if calculations fail print(f"Audio duration: {audio_duration}, Number of words: {num_words}, Word duration: {word_duration}") # Debugging subtitles = [] i = 0 while i < num_words: group = " ".join(words[i:min(i+2, num_words)]) # 2 words per group start_time = i * word_duration end_time = (i + 2) * word_duration end_time = np.clip(end_time, 0, audio_duration) # Ensure end_time doesn't exceed audio duration subtitles.append(((start_time, end_time), group)) i += 2 print("First 5 subtitles:") for i in range(min(5, len(subtitles))): print(subtitles[i]) # Create TextClips for each subtitle and concatenate them text_clips = [] for (start, end), text in subtitles: text_clip = TextClip( text, fontsize=45, # Adjust as needed color='yellow', stroke_color='#FFE629', stroke_width=1, font='Trebuchet-MS', #You can also use Arial method='caption', size=video_clip.size # Ensures correct sizing ).set_pos(('center', 'bottom')).set_start(start).set_end(end).crossfadein(0.15) text_clips.append(text_clip) final_clip = CompositeVideoClip([video_clip] + text_clips) # Add all clips return final_clip class VideoGeneratorGUI: def __init__(self, master): self.master = master master.title("Video Generator") self.title_label = tk.Label(master, text="Title:") self.title_label.grid(row=0, column=0, sticky="w", padx=5, pady=5) self.title_entry = tk.Entry(master, width=50) self.title_entry.grid(row=0, column=1, columnspan=3, sticky="we", padx=5, pady=5) self.generate_button = tk.Button(master, text="Generate", command=self.generate_text) self.generate_button.grid(row=1, column=0, padx=5, pady=5) self.regenerate_button = tk.Button(master, text="Regenerate", command=self.regenerate_text) self.regenerate_button.grid(row=1, column=1, padx=5, pady=5) self.text_area_label = tk.Label(master, text="Generated Text:") self.text_area_label.grid(row=2, column=0, sticky="w", padx=5, pady=5) self.text_area = scrolledtext.ScrolledText(master, width=60, height=10) self.text_area.grid(row=3, column=0, columnspan=4, sticky="nsew", padx=5, pady=5) self.generate_video_button = tk.Button(master, text="Generate Video", command=self.start_video_generation_thread) # Changed command self.generate_video_button.grid(row=4, column=0, columnspan=4, pady=10) self.progress_bar = ttk.Progressbar(master, orient="horizontal", length=300, mode="determinate") self.progress_bar.grid(row=5, column=0, columnspan=4, pady=5) self.progress_bar["maximum"] = 100 # Set maximum value for the progress bar # Configure grid weights to make the text area expandable master.grid_rowconfigure(3, weight=1) master.grid_columnconfigure(3, weight=1) self.log_window = None # Initialize log window self.progress_queue = queue.Queue() # Queue for progress updates self.caption_adder = CaptionAdder() # Instance of CaptionAdder # Start the UI update loop self.master.after(100, self.process_queue) # Check queue every 100 ms def generate_text(self): title = self.title_entry.get() generated_text = self.call_gemini_api(title) # Replace with actual API call self.text_area.delete("1.0", tk.END) self.text_area.insert("1.0", generated_text) def regenerate_text(self): title = self.title_entry.get() # Placeholder for Gemini API call (2nd version) regenerated_text = self.call_gemini_api(title, regenerate=True) # Replace with actual API call self.text_area.delete("1.0", tk.END) self.text_area.insert("1.0", regenerated_text) def call_gemini_api(self, prompt, regenerate=False): client = genai.Client(api_key="MY_API_KEY") try: if regenerate: response = client.models.generate_content(model="gemini-2.0-flash",contents={"More on " + prompt},) else: # Initial prompt response = client.models.generate_content(model="gemini-2.0-flash",contents={prompt},) if response.text: return response.text else: return "Gemini API returned an empty response." except Exception as e: return f"Error calling Gemini API: {e}" def start_video_generation_thread(self): text_prompt = self.text_area.get("1.0", tk.END).strip() if not text_prompt: messagebox.showerror("Error", "Text area is empty. Please generate text first.") return # Open progress dialogue before starting the video generation process self.open_progress_dialogue() # Create a thread to run the video generation process self.video_thread = threading.Thread(target=self.video_generation_task, args=(text_prompt,)) self.video_thread.daemon = True # Allow the main thread to exit even if this thread is running self.video_thread.start() def video_generation_task(self, text_prompt): """This function runs in a separate thread.""" try: self.log_message("Starting video generation...") self.progress_queue.put(10) #Initial progress update audio_file = self.text_to_speech(text_prompt) if audio_file: self.log_message("TTS successful, audio file saved.") self.log_message("Selecting random video clips...") self.progress_queue.put(30) video_clips = self.select_random_video_clips("raw") # Assuming /raw directory exists if video_clips: self.log_message("Combining video clips...") final_clip = self.combine_video_clips(video_clips, audio_file) if final_clip: self.log_message("Adding audio to video...") self.progress_queue.put(50) final_clip = self.add_audio_to_video(final_clip, audio_file) self.log_message("Adding captions...") final_clip = self.caption_adder.add_captions_to_video(final_clip, text_prompt, audio_file, progress_queue=self.progress_queue) # Pass progress_queue self.progress_queue.put(60) #Progress Update self.log_message("Rendering video...") self.render_video(final_clip, "generatedvideo.mp4") self.log_message("Video rendering complete.") self.progress_queue.put(100) #Final Progress update messagebox.showinfo("Success", "Video generated successfully!") else: self.log_message("Error: Could not combine video clips.") else: self.log_message("Error: No video clips found.") else: self.log_message("Error: TTS failed.") # Send success message to the queue self.progress_queue.put("Video generation complete!") except Exception as e: self.log_message(f"Error during video generation: {e}") self.progress_queue.put(f"Error: {e}") #Put exception message into queue finally: self.progress_queue.put("close") # Signal to close dialogue def text_to_speech(self, text_prompt): """ Calls the Bhashini TTS API to convert text to speech. Saves the response as an MP3 file. """ url = 'https://tts.bhashini.ai/v1/synthesize' data = {"text": text_prompt, "language": "English", "voiceName": "Male2"} #Other voices Male1, Male3, Female1 try: response = requests.post(url, json=data) response.raise_for_status() # Raise HTTPError for bad responses (4xx or 5xx) if response.status_code == 200: # Save the binary content to a file with open("temp_audio.mp3", "wb") as f: f.write(response.content) return "temp_audio.mp3" # Return the filename of the saved audio else: print(f"TTS API Error: {response.status_code} - {response.text}") return None except requests.exceptions.RequestException as e: print(f"TTS API Request Error: {e}") return None def select_random_video_clips(self, directory): """ Selects random video clips from the specified directory. Returns a list of video clip paths. """ try: video_files = [f for f in os.listdir(directory) if f.endswith(".mp4")] if not video_files: print(f"No MP4 files found in directory: {directory}") return None # Select a random number of videos (e.g., 3-5 clips) num_clips = random.randint(3, min(5, len(video_files))) #ensure not more videos are selected that exist selected_clips = random.sample(video_files, num_clips) full_paths = [os.path.join(directory, clip) for clip in selected_clips] return full_paths except FileNotFoundError: print(f"Directory not found: {directory}") return None except Exception as e: print(f"Error selecting random video clips: {e}") return None def combine_video_clips(self, video_paths, audio_file): """ Combines the selected video clips into a single video clip. """ try: clips = [VideoFileClip(clip) for clip in video_paths] final_clip = concatenate_videoclips(clips, method="compose") # Use 'compose' for smoother transitions return final_clip except Exception as e: print(f"Error combining video clips: {e}") return None def add_audio_to_video(self, video_clip, audio_file): """Adds audio to the video clip, adjusting video length if necessary.""" try: audio_clip = AudioFileClip(audio_file) video_duration = video_clip.duration audio_duration = audio_clip.duration # Adjust video length to match audio length if video_duration > audio_duration: video_clip = video_clip.subclip(0, audio_duration) # Trim video elif audio_duration > video_duration: # Extend video by looping it (simple example) loop_count = int(audio_duration / video_duration) + 1 video_clip = concatenate_videoclips([video_clip] * loop_count, method="compose").subclip(0, audio_duration) final_clip = video_clip.set_audio(audio_clip) return final_clip except Exception as e: print(f"Error adding audio to video: {e}") return None def render_video(self, video_clip, output_file): """Renders the final video to a file.""" try: video_clip.write_videofile(output_file, fps=24, codec="libx264", audio_codec="aac") except Exception as e: print(f"Error rendering video: {e}") def open_progress_dialogue(self): self.log_window = tk.Toplevel(self.master) self.log_window.title("Video Generation Progress") self.log_text = scrolledtext.ScrolledText(self.log_window, width=60, height=10) self.log_text.pack(padx=5, pady=5, fill=tk.BOTH, expand=True) self.log_text.config(state=tk.DISABLED) # Make it read-only def close_progress_dialogue(self): if self.log_window: self.log_window.destroy() self.log_window = None def log_message(self, message): """Logs a message to the progress dialogue.""" if self.log_window: self.log_text.config(state=tk.NORMAL) # Allow editing temporarily self.log_text.insert(tk.END, message + "\n") self.log_text.see(tk.END) # Scroll to the end self.log_text.config(state=tk.DISABLED) # Disable editing def process_queue(self): """Updates the UI based on messages in the queue.""" try: while True: message = self.progress_queue.get_nowait() # Non-blocking get if isinstance(message, int): # Update progress bar self.progress_bar["value"] = message elif message == "close": self.close_progress_dialogue() elif "Error:" in message: messagebox.showerror("Error", message) #Display Error self.log_message(message) #Also log it to the log window else: # Update log message self.log_message(message) self.master.update_idletasks() #Update UI except queue.Empty: pass # No message in the queue self.master.after(100, self.process_queue) # Check the queue again after 100ms root = tk.Tk() gui = VideoGeneratorGUI(root) root.mainloop()





0 Please Share a Your Opinion.:
Comment something useful and creative :)